RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) GPS technology has revolutionized precise positioning in fields such as agriculture, surveying, construction, and autonomous vehicles. However, the accuracy of RTK GPS relies heavily on correction signals. Understanding rtk gps corrections—specifically NTRIP, radio, and cellular—is essential for anyone looking to leverage high-precision GPS technology.
What is RTK GPS?
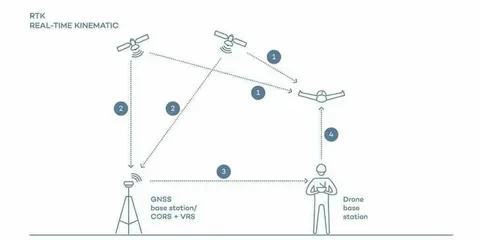
RTK GPS enhances the accuracy of standard GPS from a few meters to the centimeter level by using real-time correction data. This data is provided by a base station with a known location, which communicates with a rover (the GPS receiver in the field). Without correction signals, GPS positioning can be inaccurate due to atmospheric interference, satellite errors, and multipath effects.
Methods of RTK GPS Corrections
There are three primary methods for delivering RTK GPS corrections: NTRIP, radio, and cellular. Each method has its advantages and limitations depending on the application and environment.
NTRIP (Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol)
NTRIP is a popular method for receiving RTK corrections over the internet. It relies on a network of reference stations to provide real-time correction data to GPS rovers through a mobile or internet connection.
Advantages of NTRIP:
- Wide coverage in areas with internet access.
- Easy to integrate with mobile devices and RTK receivers.
- Access to corrections from multiple reference stations, improving accuracy.
Limitations:
- Requires reliable internet connectivity.
- Data latency may affect precision in remote areas with poor signal coverage.
Radio-Based RTK Corrections
Radio RTK corrections use radio frequencies to transmit data from a base station directly to a rover. This method is highly reliable in areas with limited internet connectivity and is widely used in agricultural and construction operations.
Advantages of Radio RTK:
- Low latency and high reliability.
- Effective in remote locations without cellular coverage.
Limitations:
- Limited range depending on the radio power and terrain.
- Requires line-of-sight between base and rover for optimal performance.
Cellular RTK Corrections
Cellular networks can also be used to deliver RTK GPS corrections. This method leverages existing mobile networks, allowing rovers to receive correction data in real-time without the need for a dedicated radio system.
Advantages of Cellular RTK:
- Large coverage area in urban and suburban regions.
- No need for setting up personal base stations.
Limitations:
- Dependence on mobile network availability and stability.
- Potentially higher latency compared to direct radio transmission.
Choosing the Right Correction Method
When deciding on the best RTK correction method, it is essential to consider your operational environment, budget, and accuracy requirements. For example:
- NTRIP is ideal for users who have reliable internet access and need corrections from multiple base stations.
- Radio RTK is preferred for remote or large-scale agricultural areas.
- Cellular RTK is suitable for urban and suburban settings with good mobile network coverage.
Conclusion
Understanding RTK GPS corrections: NTRIP, radio, and cellular is crucial for maximizing the accuracy and reliability of GPS applications. Each method offers distinct benefits and trade-offs, and selecting the right one ensures optimal performance in your specific use case. By carefully evaluating your operational environment and connectivity options, you can harness the full potential of RTK GPS for precise and efficient positioning.